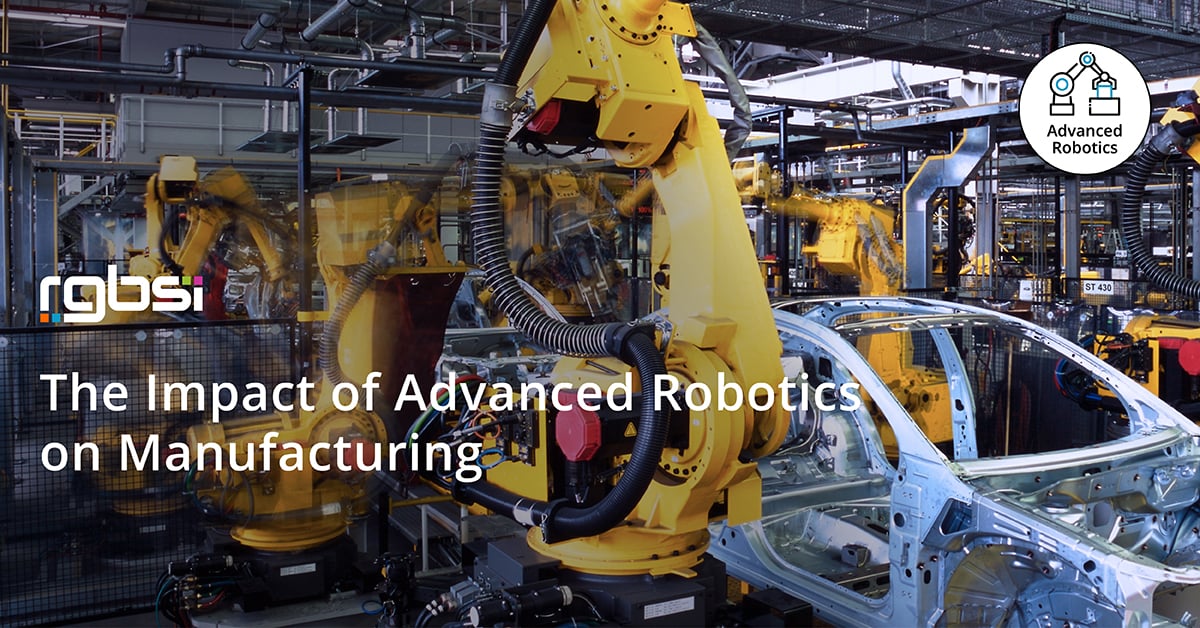
What are advanced robotics?
Advanced robotics are a combination of sophisticated programming and powerful hardware that make use of smart sensor technology (including ultrasonic, touch, and light sensors) to interact with the real world around it. In Industry 4.0, advanced robotics is used in manufacturing facilities that sometimes run without human oversight around the clock.
According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), 2.1 million industrial robots were in operation worldwide as of 2017. There a few different types of industrial robots: articulated robots, collaborative robots, selective compliance assembly robots, and automated guided vehicles among others.
Advanced robotics are making an impact on manufacturing. As manufacturing processes increase in complexity and scope thanks to digitization and the application of advanced computing technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) to more areas of product design, manufacturing, supply chain, and retail. Applications of advanced robotics are being used with increasing frequency to help streamline and simplify initiatives. This new more complicated operating environment demands an increasing amount of automation.
Advanced Robotics and the Job Market
The transformation of traditional labor into robotic optimized labor will continue to transition as we move into the future. It is debatable whether or not advanced robotics are a cause for concern in displacing manufacturing jobs. Robotics can also change the job market positively by opening up opportunities that demand different types of skillsets.
For example, the use of robots in manufacturing restores more manufacturing procedures and helps create jobs that way. They help reduce repetitive, boring, and dangerous work. They have the potential to create more desirable jobs such as equipment maintenance and management, but also move new jobs into fields that require a higher degree of specialization and training like engineering and programming.
In response to the changing manufacturing environment, companies look for ways to develop talent further in prediction of future business requirements. RGBSI recently installed a robotics training center named “RGBSI Robotics & Automation Center” at Goodwin College to better prepare students for the evolving skillset demands in advanced robotics and digital engineering.
How does Industry 4.0 use advanced robotics?
Industry 4.0 uses advanced robotics to increase productivity by taking over manual tasks and accomplishing them faster, which is known as the factory of the future. The assembly of flexible parts is one example. Advanced robots can do this because they have the ability to adjust themselves and course correct when procedures and processes change. Conventional robots in an industrial setting do not have this type of adaptability. If procedures or processes change on the assembly line with conventional robots, they have to briefly stop for reconfiguration.
In addition, use of advanced robots offer another advantage over conventional robots in that they are easier to set up and configure on an assembly line from the beginning of their implementation. Advanced robots can also take advantage of simulation software to learn how to perform an array of tasks. This is a desirable attribute for companies that use production systems which require many adjustments during the course of production.
On the assembly line, manufacturers improve quality, reliability, and precision by closing skills gaps with technology. They are also much safer than their conventional robot counterparts at working in hazardous environments. Conventional robots are less safe for humans to work with compared to advanced robots. Many advanced robots actively “perceive” their environment with machine vision and smart sensor technology.
Digitizing manufacturing environments offers more configurable, flexible, and adaptable production systems. Advanced robotics allow manufacturers to respond to the increasing demand for customized products and single product variations.
What is Lights-Out Manufacturing?
But Industry 4.0 is about the convergence of multiple advanced technologies in industrial setting, and perhaps no manufacturing facility embodies Industry 4.0 more than Japan’s FANUC. At FANUC, robots produce other robots without the presence of humans.
This is called lights-out manufacturing, and these types of facilities are on the rise worldwide. This type of operational practice requires 100% certainty in any given manufacturing process.
About RGBSI
At RGBSI, we deliver total workforce management, engineering, quality lifecycle management, and IT solutions that provide strategic partnership for organizations of all sizes.
Engineering Solutions
As an organization of engineering experts, we understand the importance of modernization. By pairing modern technology with design expertise, we elevate fundamental engineering principles to accommodate growing product complexity requirements. We work with clients to unlock the full potential of their products and enable future innovation. Learn more about our automation and digital engineering services.
IT Solutions
We work with clients to support IT related areas of application development, ERP, infrastructure, project management, and digital engineering.
Learn more about our IT solutions.











